Core Value: The “Safety Cornerstone” for Stable Kiln Operation
Kilns often face high-temperature environments exceeding 1000℃ during operation, while simultaneously enduring multiple challenges such as material erosion, chemical corrosion, and sudden temperature changes. Kiln fire bricks, through their superior material properties, achieve three core functions:
First, thermal insulation, reducing heat loss within the kiln, lowering energy consumption, and improving thermal efficiency;
Second, corrosion resistance, protecting the kiln shell from molten materials, slag, and corrosive gases, preventing deformation or damage;
Third, structural support, maintaining the kiln’s internal structure, ensuring stable material flow, and improving production continuity. High-quality fire bricks can extend kiln maintenance cycles by more than 30%, significantly reducing downtime losses and creating higher economic benefits for enterprises.
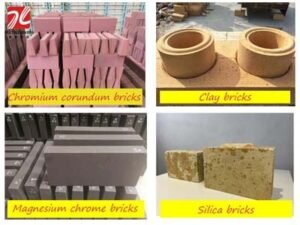
Core Classifications and Characteristics: Precisely Matching Different Working Conditions
Based on differences in material composition and performance, kiln fire bricks can be divided into six core categories. Each category is specifically adapted to different temperatures, atmospheres, and corrosive conditions. Specific characteristics are as follows:
Clay Fire Bricks
Cost-effective choice, suitable for medium and low temperature conditions. Made primarily from high-quality fireclay, with an alumina content of 30%-48%, and a refractoriness of 1580℃-1770℃, they possess excellent thermal stability and thermal shock resistance, while maintaining relatively low cost. Suitable for medium and low temperature kilns with temperatures ≤1300℃. Such as brick and tile tunnel kilns and hot blast stove preheating sections. They are the most widely used basic fire brick category in industrial production.
High-Alumina Fire Bricks
High-Temperature General-Purpose, Balancing Performance and Adaptability. Made from high-purity bauxite with an alumina content of 48%-90%, this type of fire brick boasts a refractoriness of 1770℃-2000℃, exhibiting superior high-temperature resistance, erosion resistance, and mechanical strength compared to clay-based fire bricks. Suitable for high-temperature kilns operating at 1200℃-1600℃. Such as the transition zone of cement rotary kilns, the high-temperature section of ceramic firing kilns, and metallurgical heating furnaces. It is a core general-purpose fire brick for high-temperature kilns.
Siliceous Fire Bricks
Specifically designed for acidic environments, offering excellent resistance to acid erosion. With a silica content ≥93% and a refractoriness of 1690℃-1730℃, its core advantages include extremely strong resistance to acidic slag and gas erosion, high load softening temperature, and good structural stability. Specifically suited for acidic atmosphere kilns. Such as coke oven carbonization chambers, glass melting furnace regenerators, and acidic steelmaking furnaces. It effectively resists the erosion of kiln linings by acidic materials.
Magnesia Fire Bricks
The King of Alkaline High-Temperature Resistance, Extremely High-Temperature and Erosion Resistant. Made from high-quality magnesite with a magnesium oxide content ≥80%, these bricks boast a refractoriness exceeding 2000℃, making them one of the best high-temperature resistant fire brick types currently available. They exhibit exceptional resistance to alkaline slag erosion. Suitable for alkaline atmosphere kilns operating at 1500℃-1800℃. Such as metallurgical open-hearth furnaces, non-ferrous metal smelting kilns, and cement rotary kiln firing zones, among other high-temperature and highly erosive conditions.
